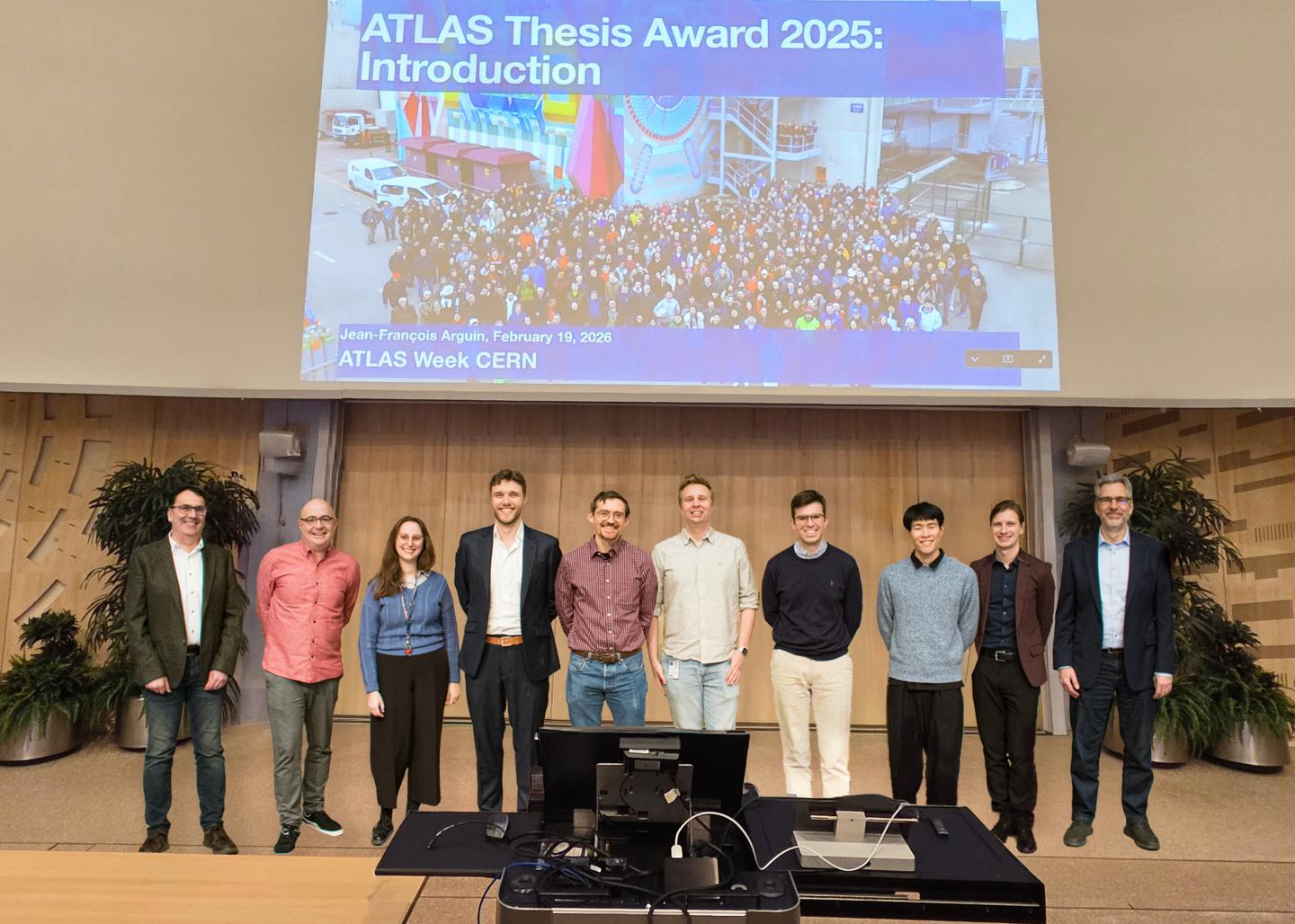
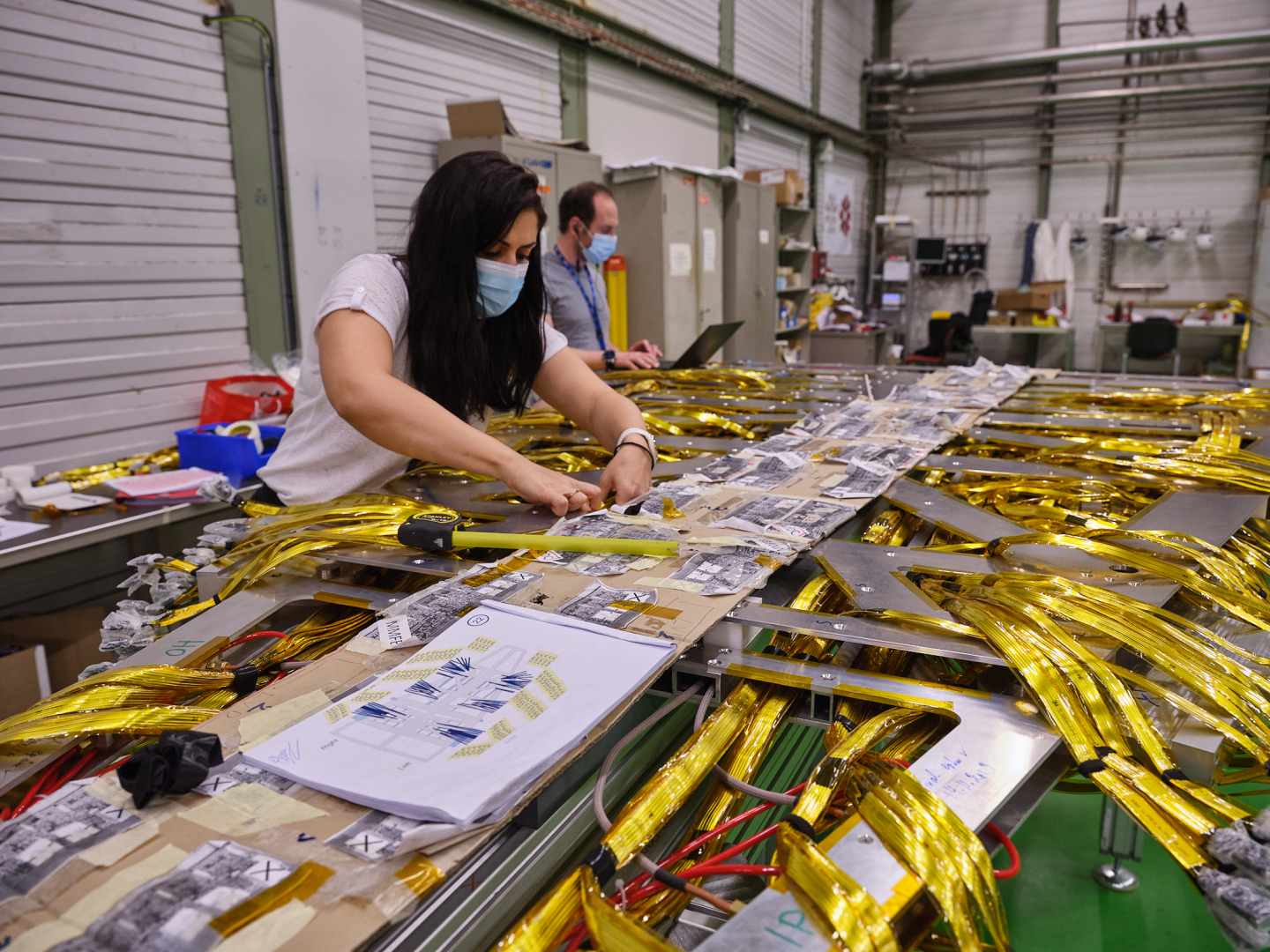
ATLAS recognises the outstanding achievements of Collaboration members
News |
ATLAS finds evidence of a rare Higgs boson Dalitz decay to two leptons and a photon
Teaching university students with real ATLAS data
Blog |
2020: an unprecedented year in review
News |
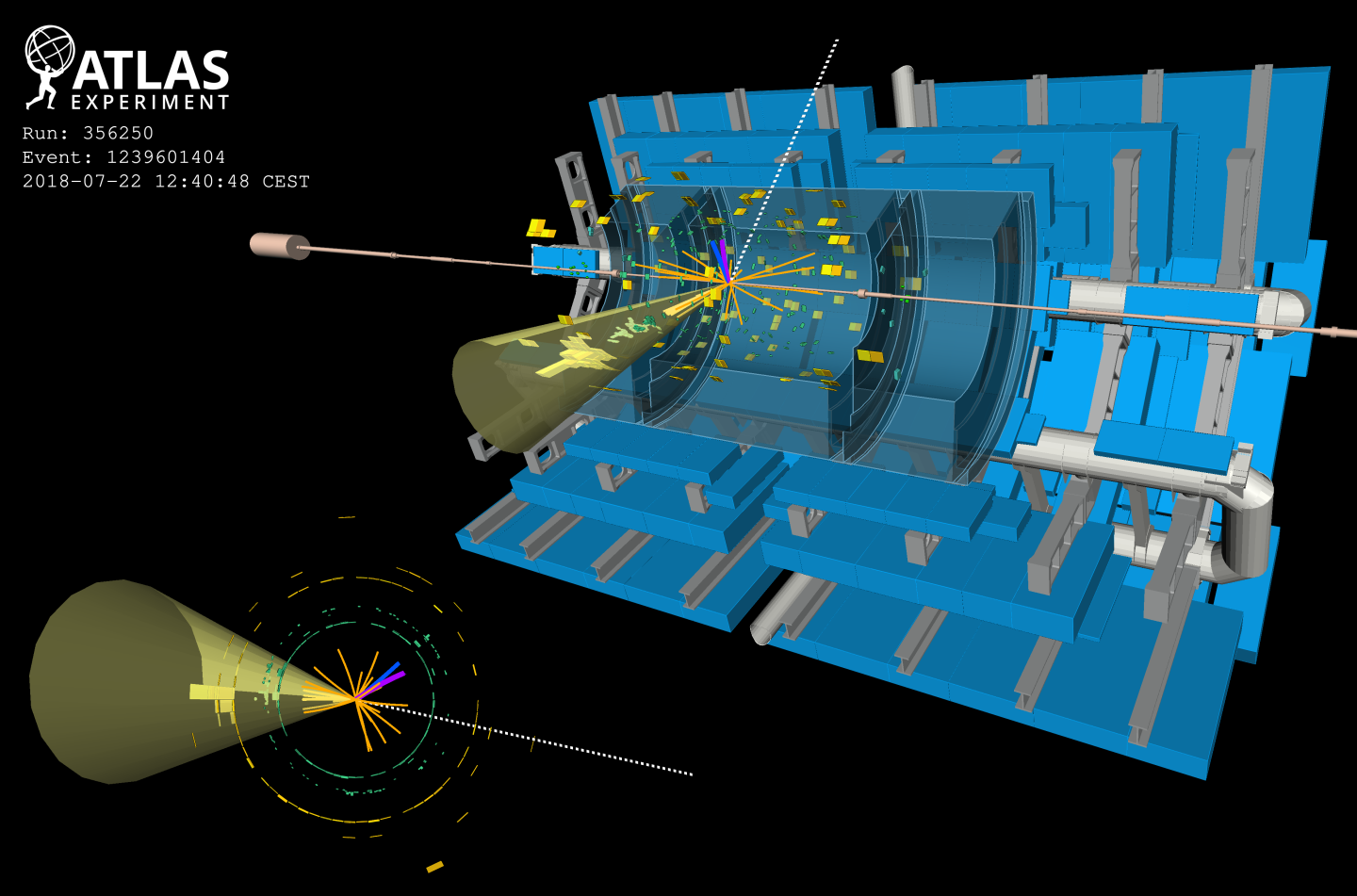
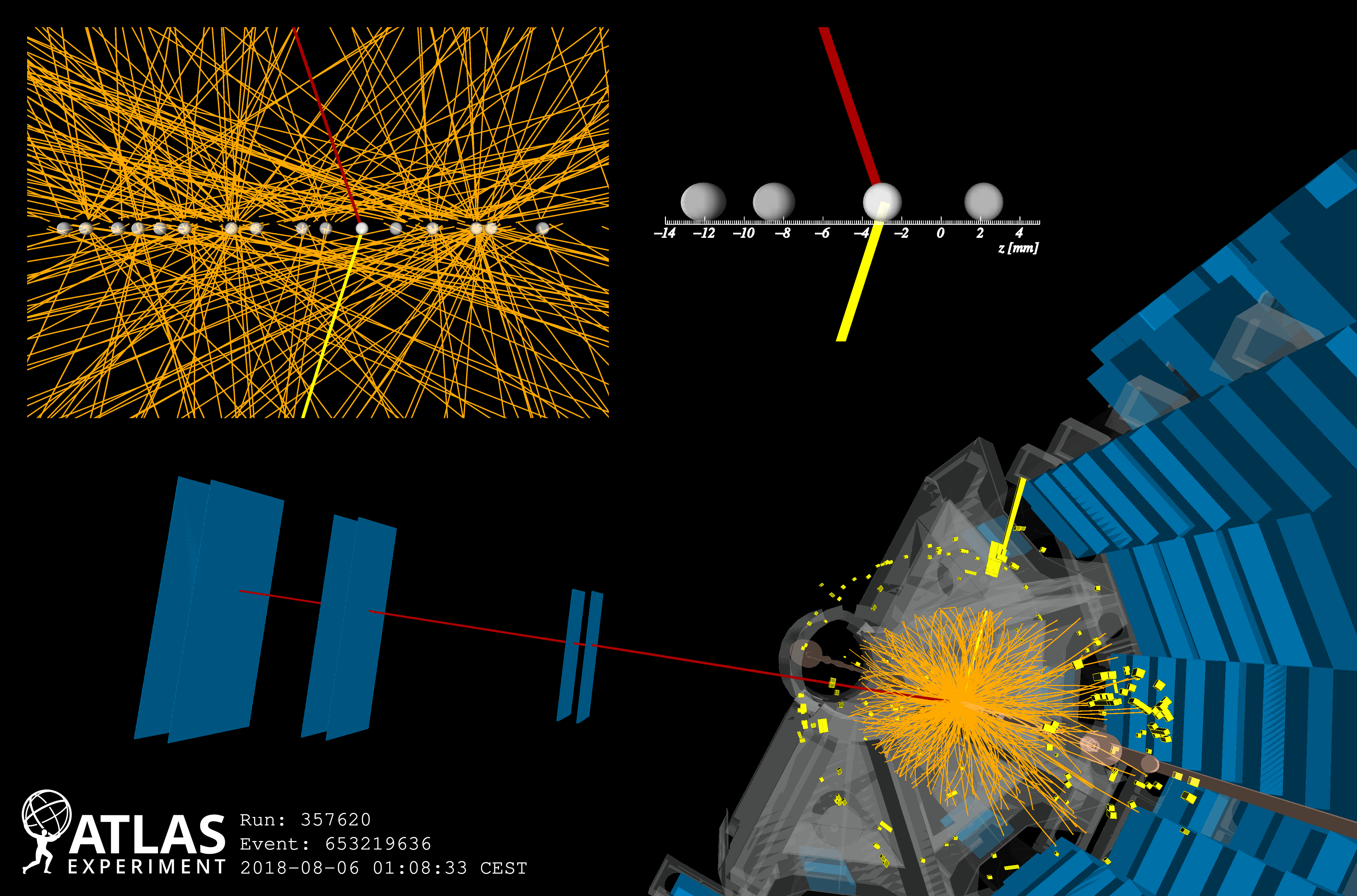
Studying the Higgs boson in its most common – yet uncommonly challenging – decay channel
ATLAS Live talk: How elementary particles are detected with Prof. Daniela Bortoletto
News |
ATLAS releases new open software
The ATLAS Collaboration has just released a collection of 200 software packages that make up the Trigger and Data Acquisition System (TDAQ). With this new release, most ATLAS software is now open – reinforcing the Collaboration’s ongoing commitment to open science.
News |
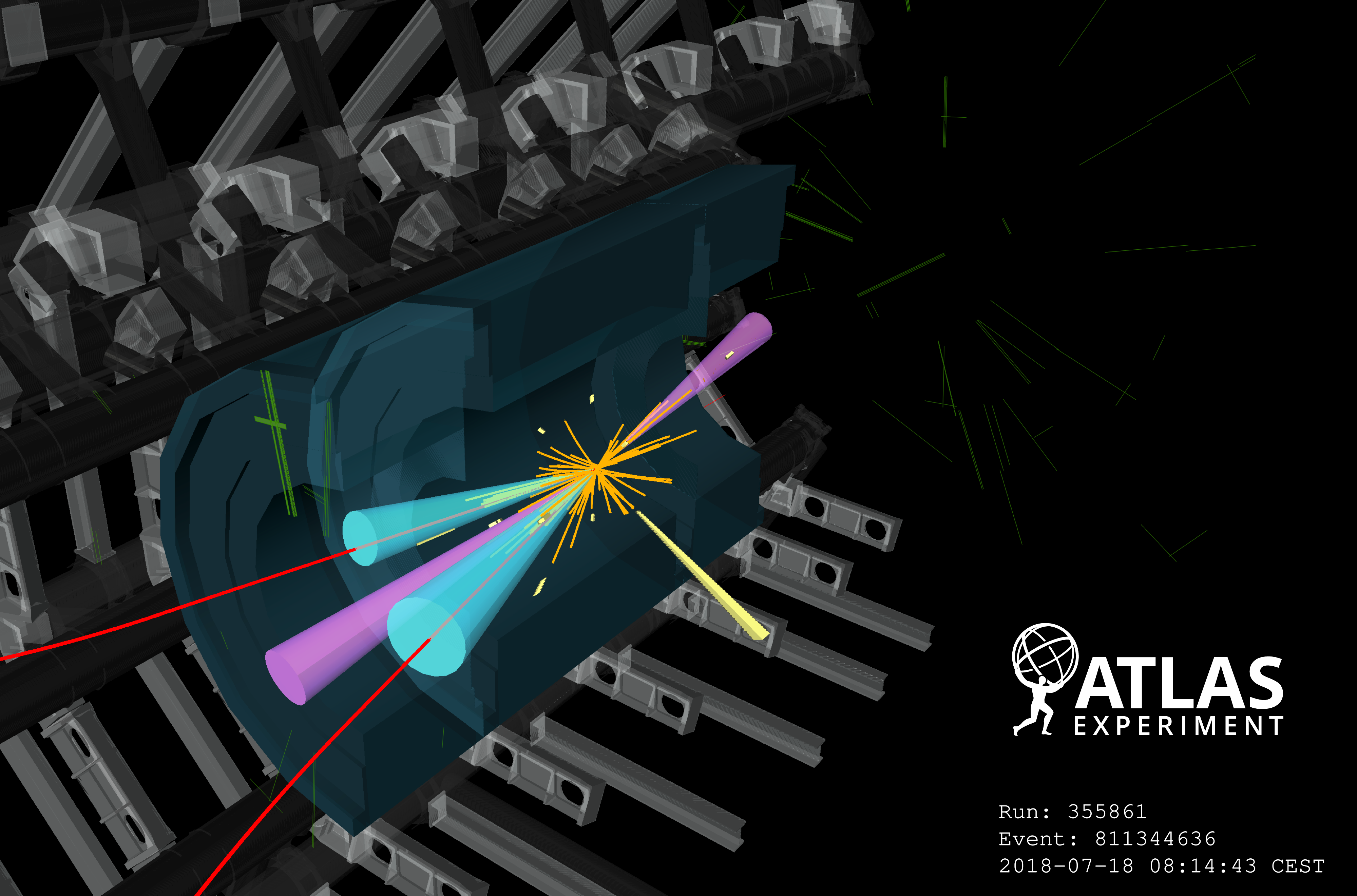
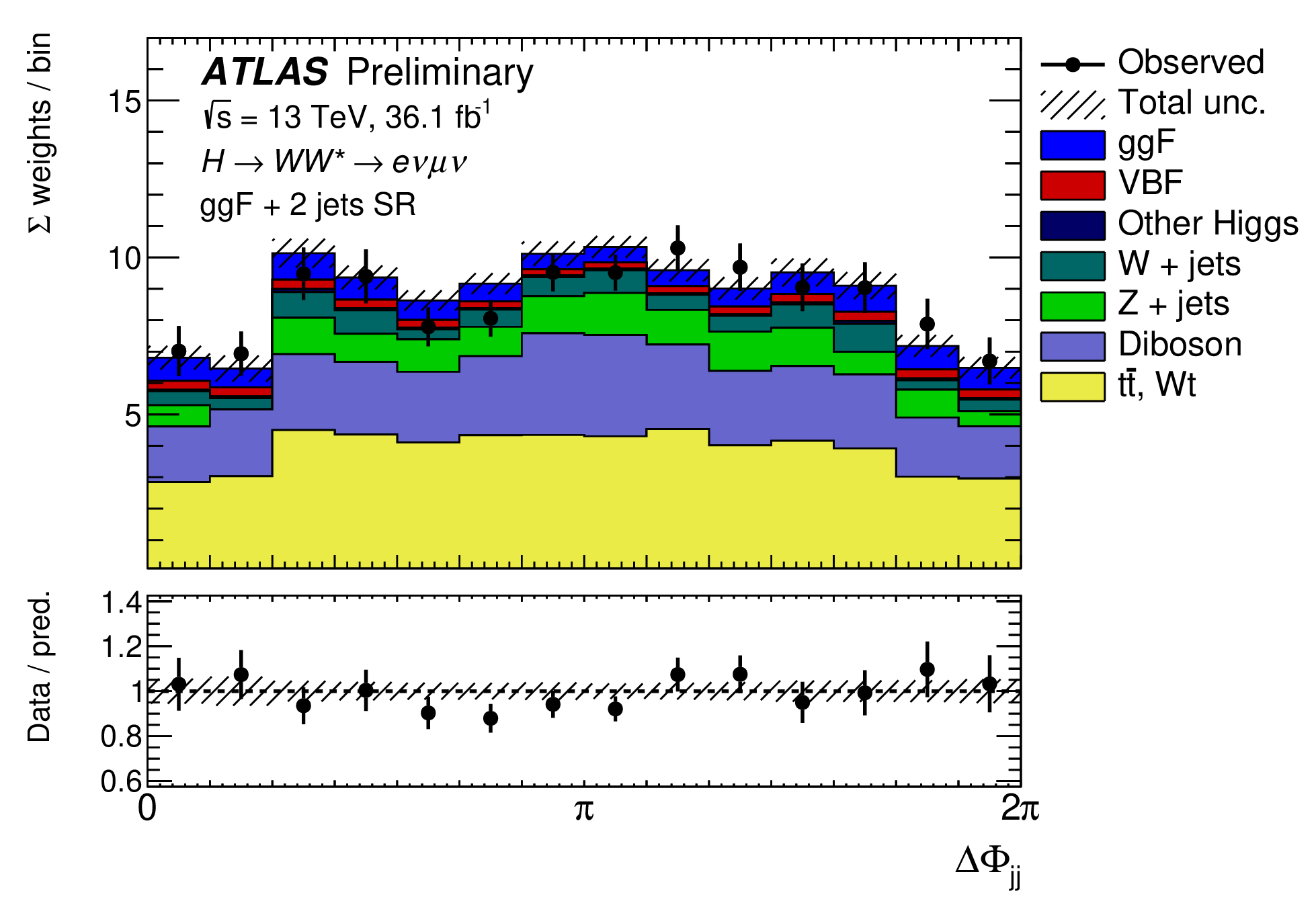
Refining the picture of the Higgs boson
A new result from the ATLAS Collaboration, released for the Higgs 2020 conference, aims at enriching the Higgs picture by studying its WW* decays.
ATLAS Live talk: Searching for Dark Matter with Dr. Christian Ohm
News |
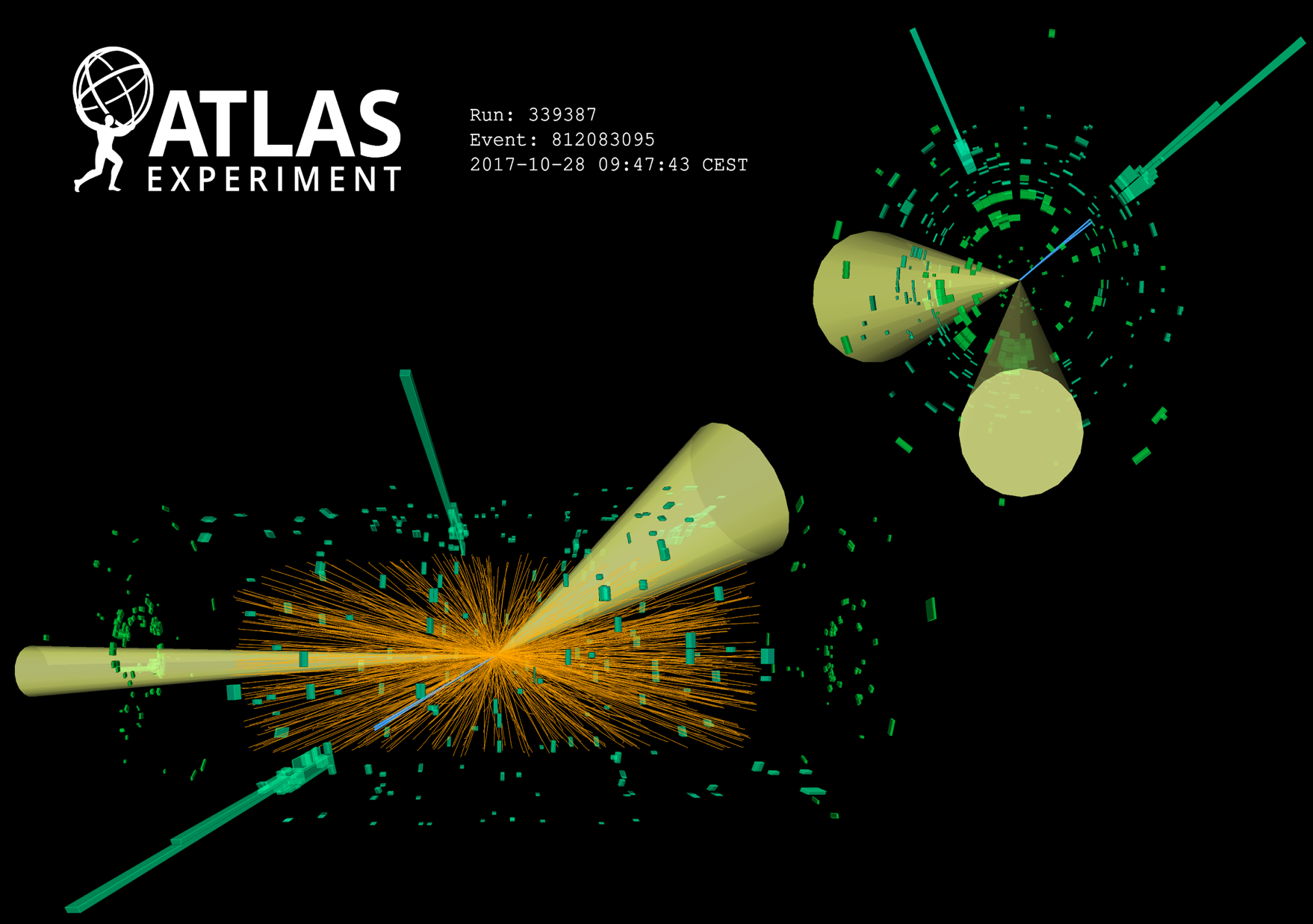
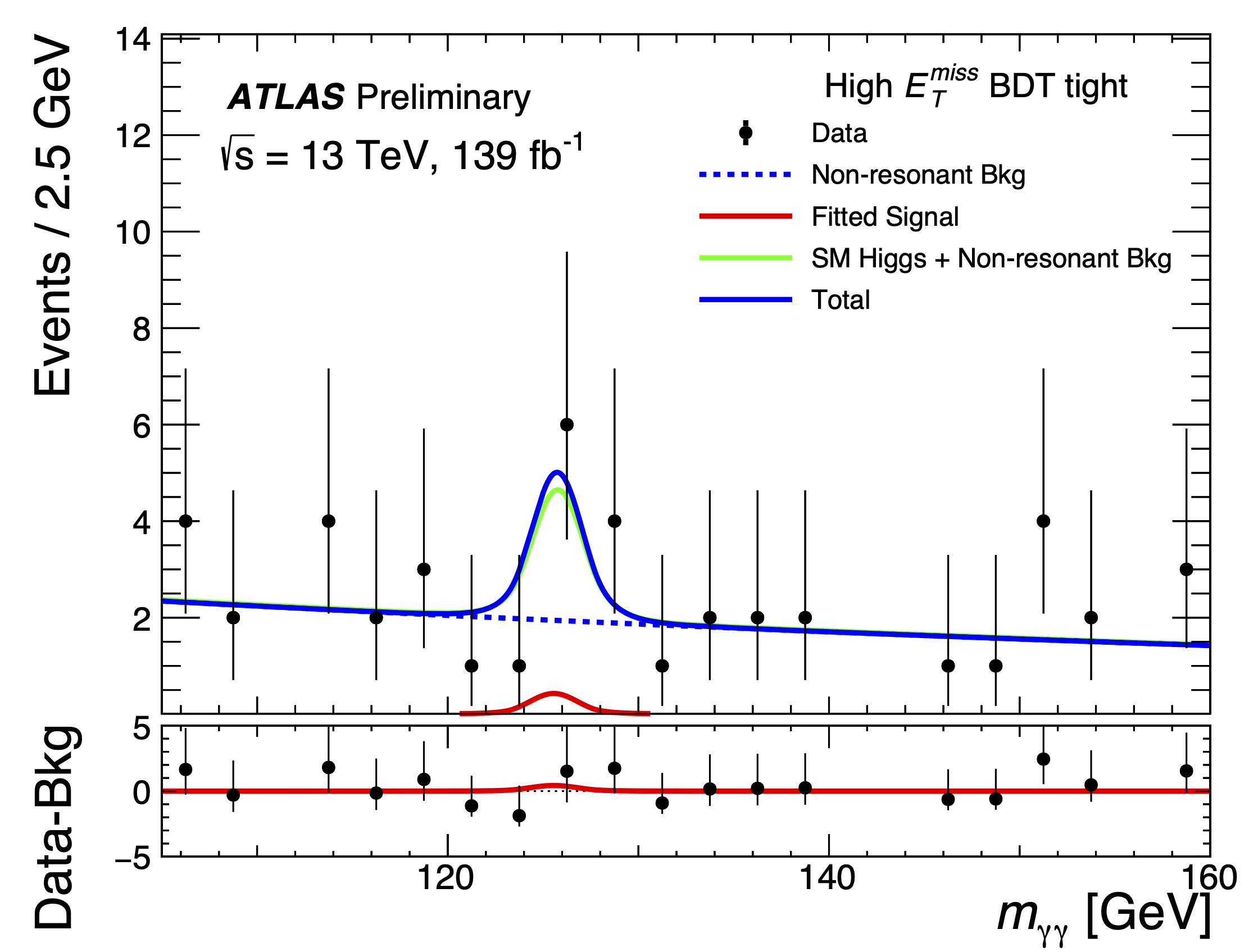
ATLAS uses the Higgs boson as a tool to search for Dark Matter
One of the great unexplained mysteries is the nature of dark matter. So far, its existence has only been established through gravitational effects observed in space; no dark-matter particles with the needed properties have (yet) been detected. Could the Higgs boson be the key to their discovery?
Higgs boson probes for new phenomena
ATLAS scientists are implementing a new strategy in the search for physics beyond the Standard Model – one that combines measurements across the full spectrum of the Collaboration's research programme.
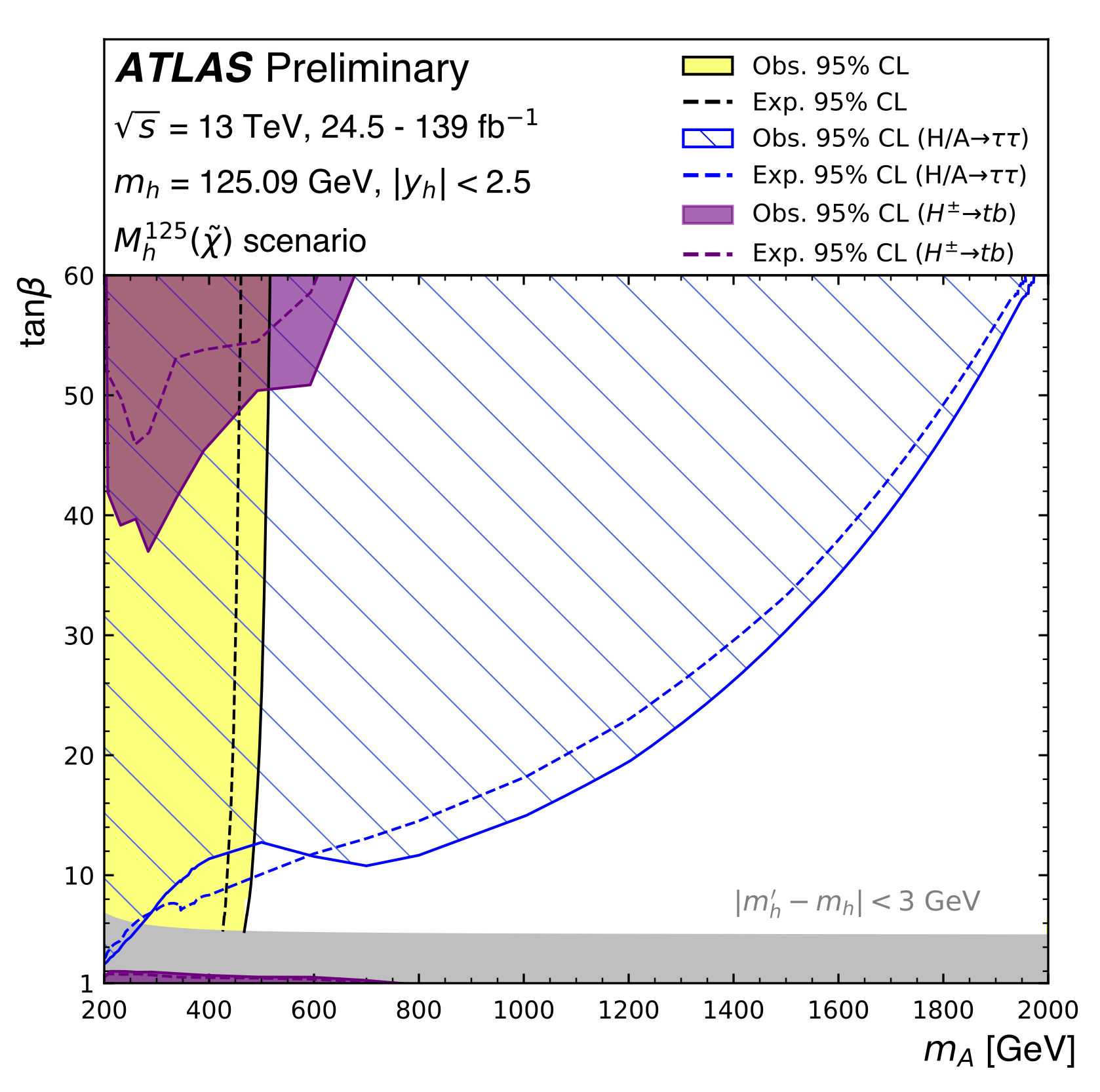
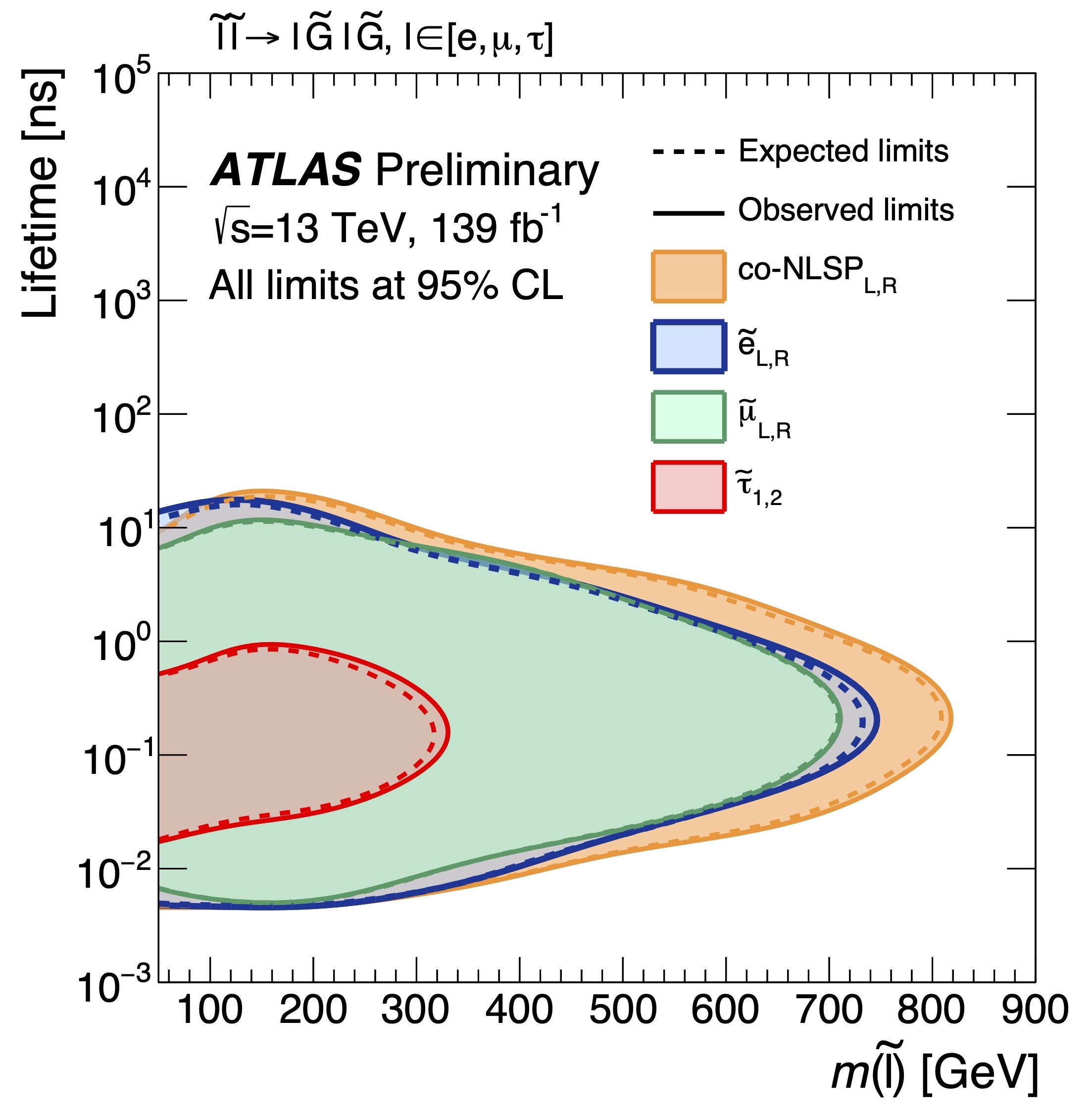
Leptons at a distance: a new search for long-lived particles
ATLAS researchers are broadening their extensive search programme to look for more unusual signatures of unknown physics, such as long-lived particles. A theory that naturally motivates long-lived particles is supersymmetry (SUSY). A new search from the ATLAS Collaboration – released this week for the 5th International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics (ICPPA-2020) – looks for the superpartners of the electron, muon and tau lepton
Unraveling Nature's secrets: vector boson scattering at the LHC
In 2017, the ATLAS and CMS Collaborations announced the detection of a never-before-observed process: vector boson scattering.
Feature |
Exploring the “coolest” mock-up
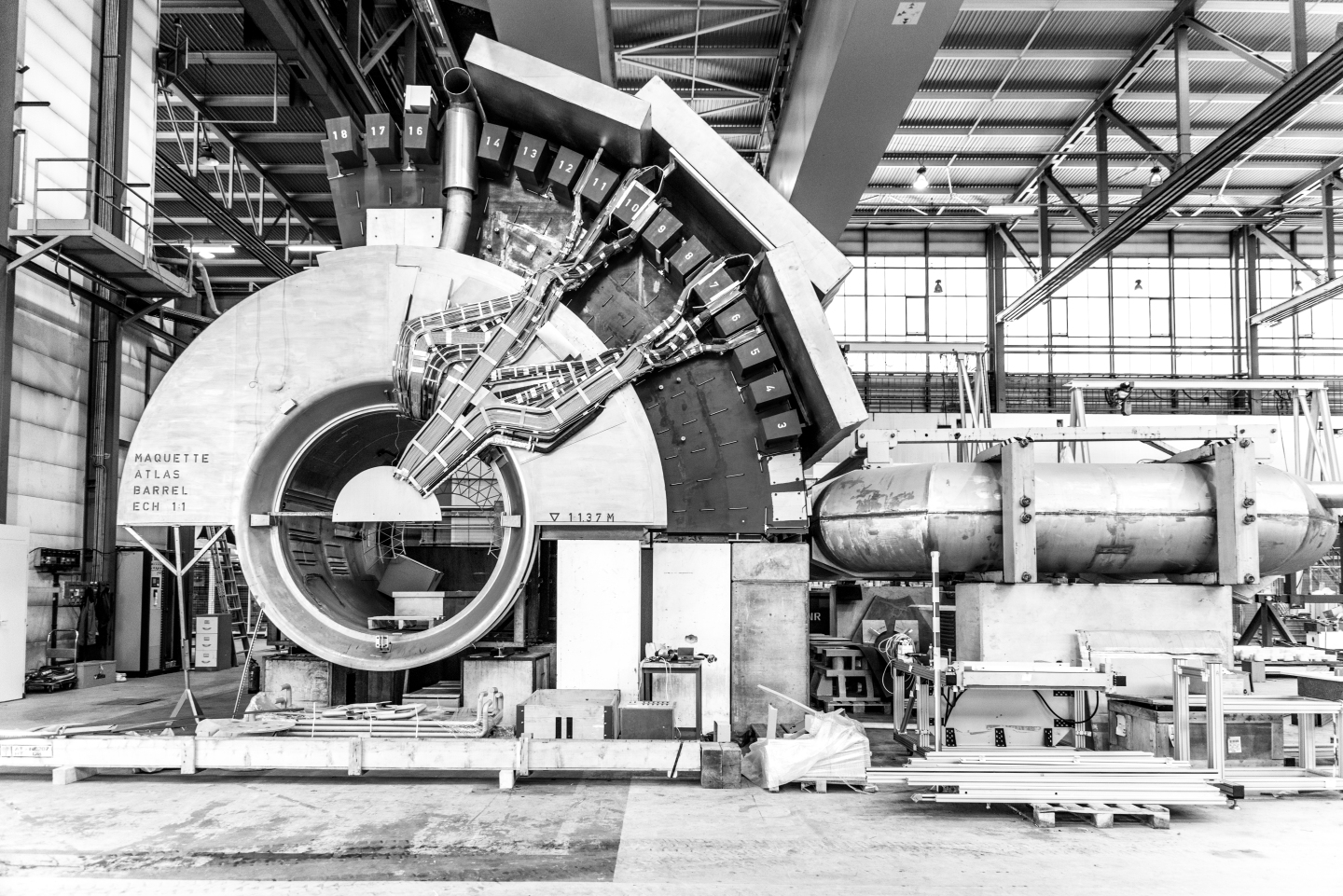
It was in 2014, just a few months after my transition from ALICE to ATLAS, that I saw the mock-up for the first time: a full-scale wooden reproduction of the central portion of the ATLAS experiment, measuring some 8 metres high and wide.
Blog |
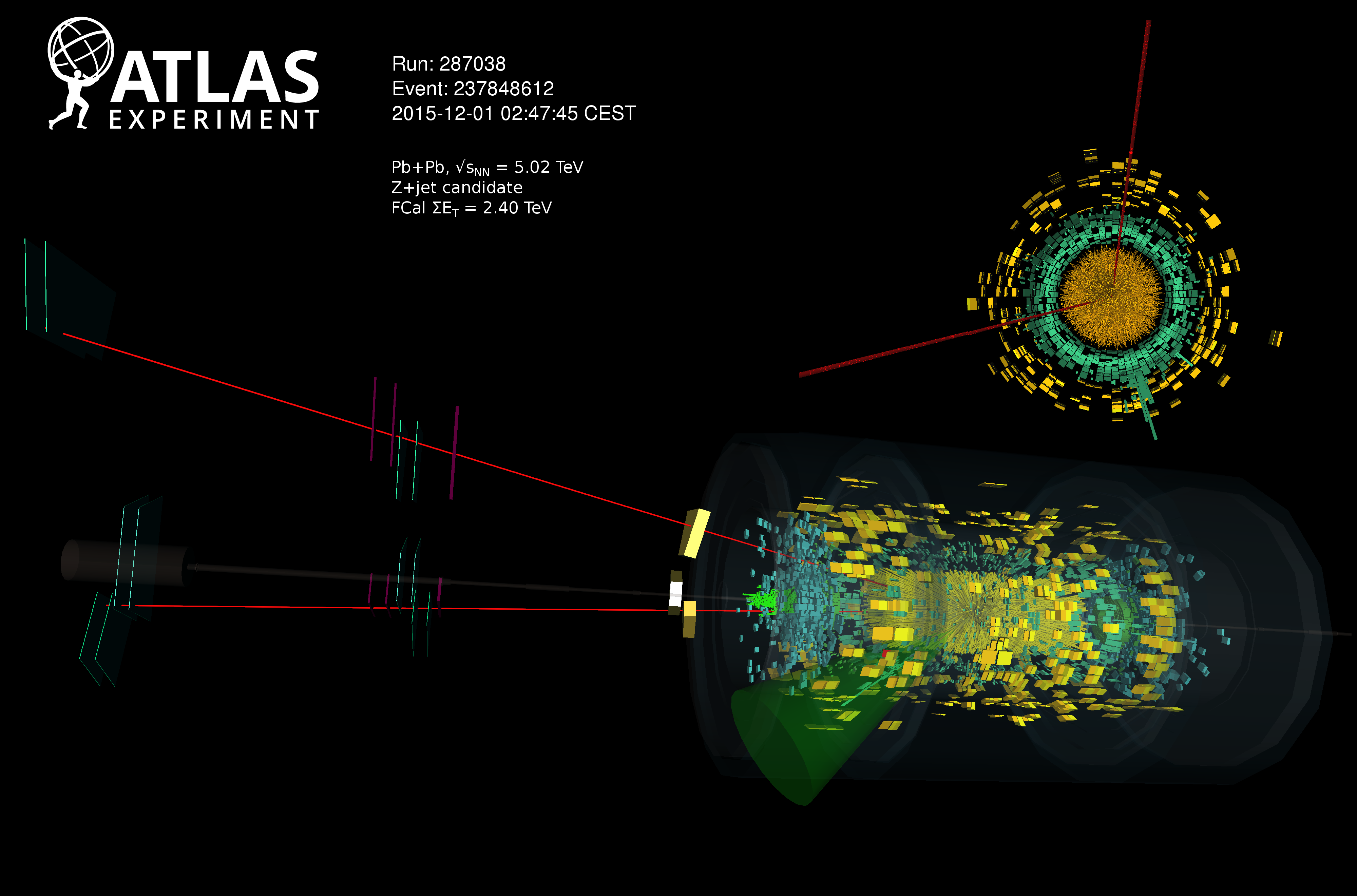
Z bosons zoom through quark–gluon plasma as jets quench
With new data from the LHC, ATLAS physicists have measured jet-quenching phenomena in the quark–gluon plasma with help of Z bosons.
ATLAS highlights presented at the world's largest particle-physics conference
As major players in the field of particle physics, the LHC collaborations contributed many new results, most of which exploited the full Run-2 dataset, recorded in 2015 to 2018. ATLAS physicists contributed 35 new results, and gave 85 talks in the parallel and plenary sessions. Their contributions spanned a wide range of topics, from precision measurements and searches for new phenomena to detector performance and R&D, as well as diversity and outreach.
News |
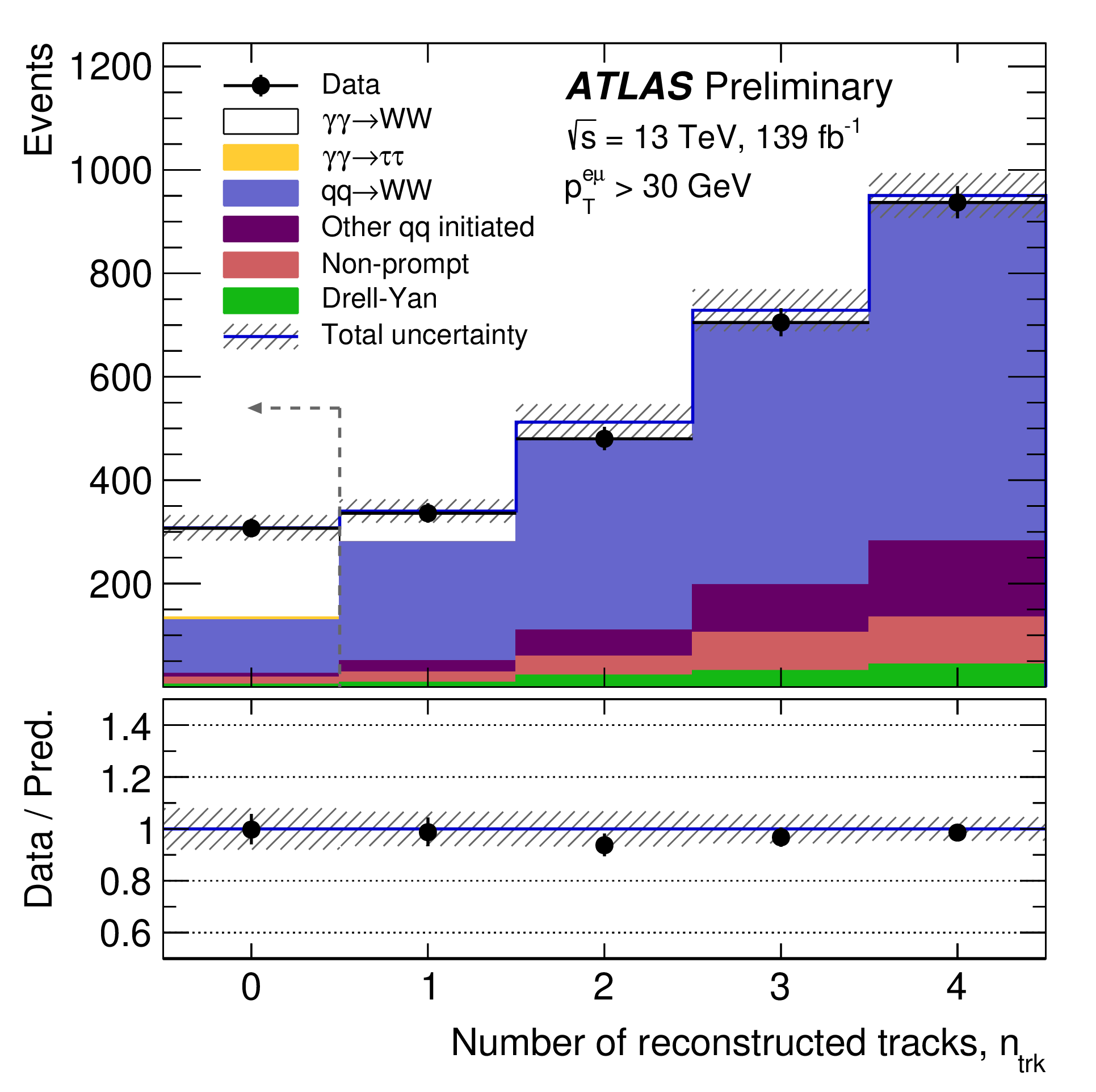
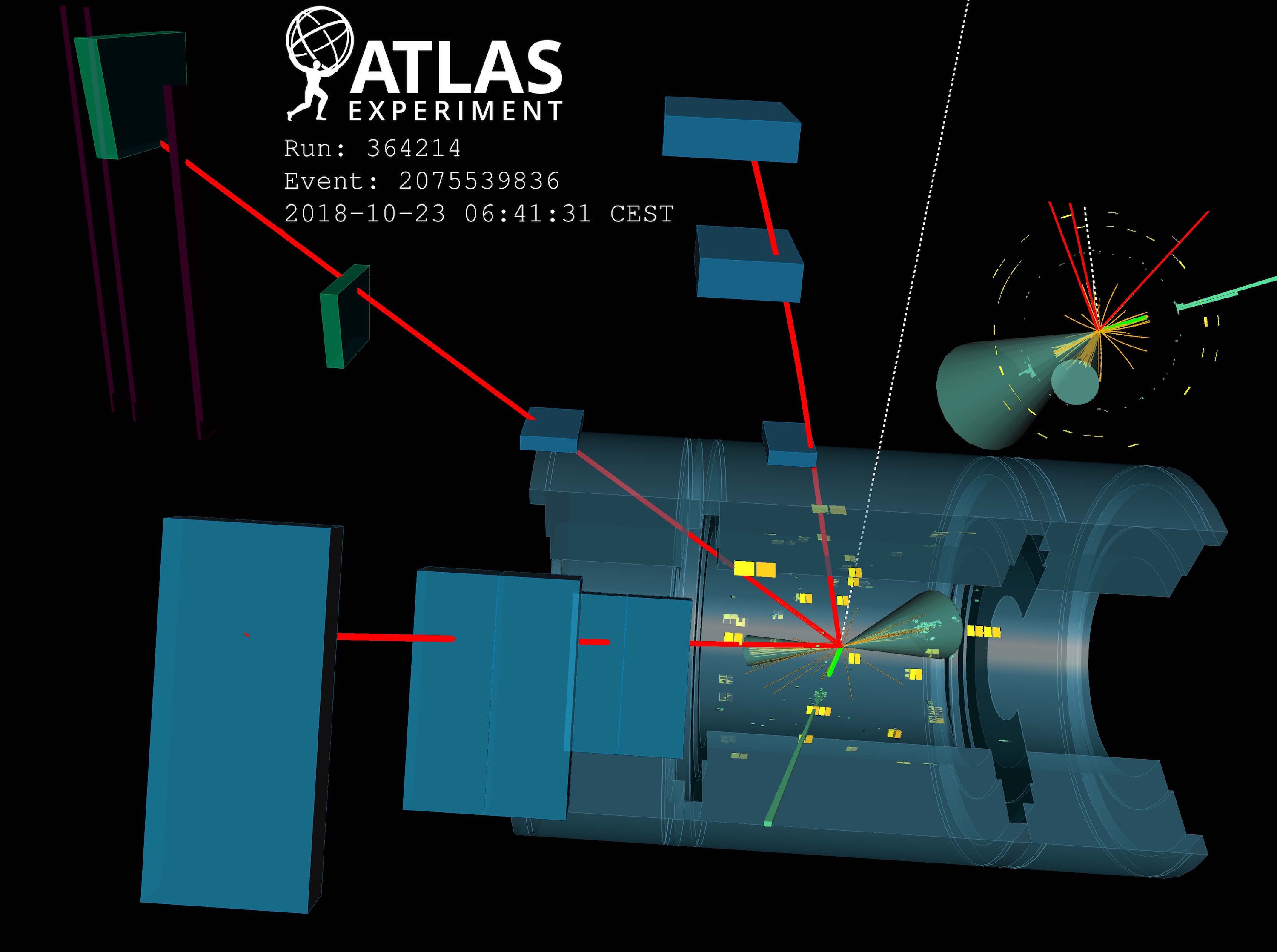
Rare phenomenon observed by ATLAS features the LHC as a high-energy photon collider
During the International Conference on High-Energy Physics (ICHEP 2020), the ATLAS Collaboration presented the first observation of photon collisions producing pairs of W bosons, elementary particles that carry the weak force, one of the four fundamental forces. The result demonstrates a new way of using the LHC, namely as a high-energy photon collider directly probing electroweak interactions. It confirms one of the main predictions of electroweak theory – that force carriers can interact with themselves – and provides new ways to probe it.
ATLAS observes W-boson pair production from light colliding with light
The ATLAS Collaboration has announced the first observation of two W bosons produced from the scattering of two photons — particles of light – at the International Conference on High-Energy Physics (ICHEP 2020).
CERN experiments announce first indications of a rare Higgs boson process
The ATLAS and CMS experiments at CERN announce new results which show that the Higgs boson decays into two muons. These new results have pivotal importance for fundamental physics because they indicate for the first time that the Higgs boson interacts with second-generation elementary particles.
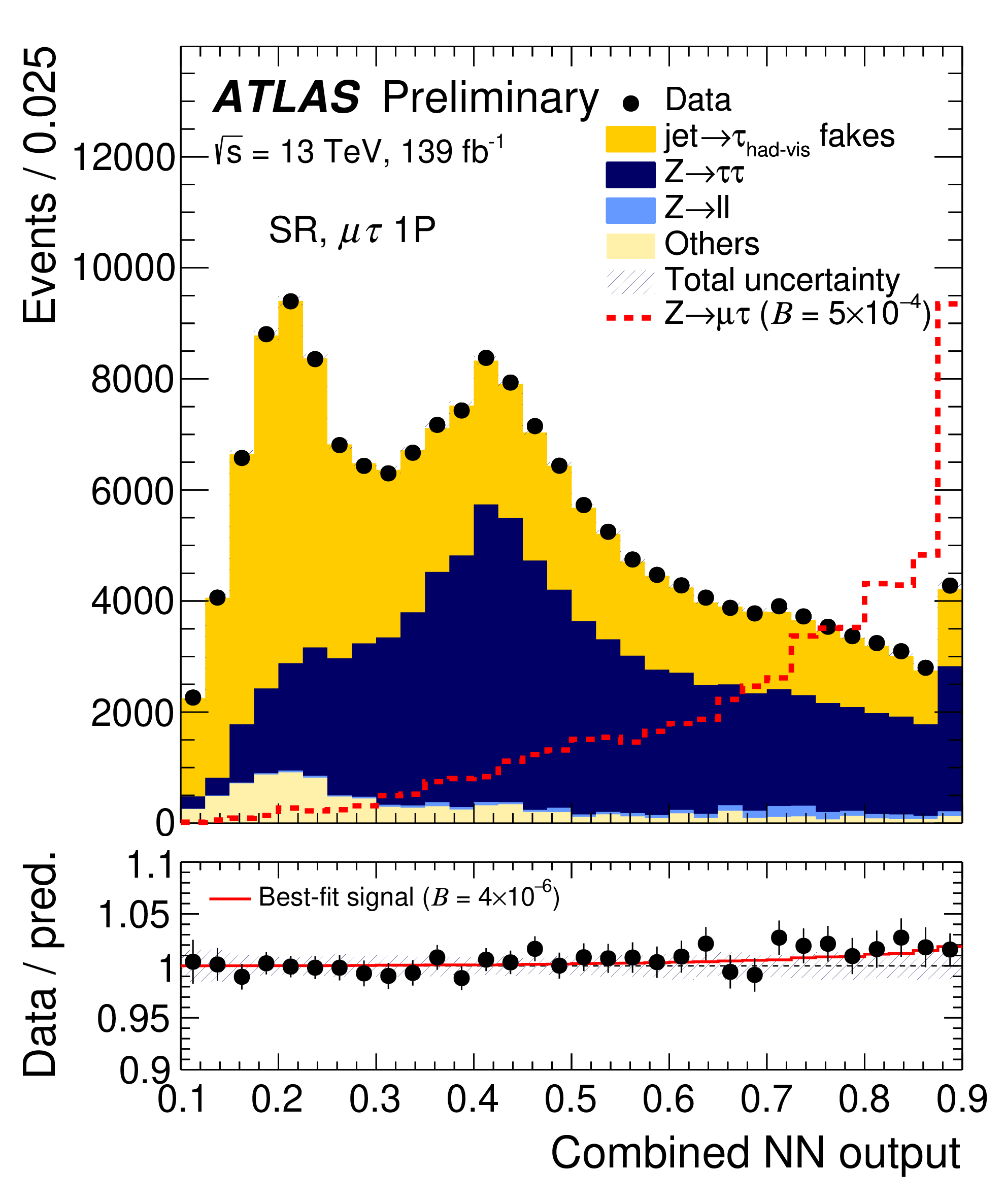
New ATLAS result marks milestone in the test of Standard Model properties
The ATLAS Collaboration has released a new study into a key building block of matter: leptons. This type of particle comes in three different families (flavours) and, according to the Standard Model, should follow strict rules. For instance, except for their mass, leptons of different flavours have identical properties – a feature known as lepton flavour universality. This was recently corroborated by a key measurement of the W-boson decay rates into leptons by the ATLAS Collaboration.
New measurements of the Higgs boson find strength in unity
Physicists can study Higgs-boson couplings in several ways: by measuring the rates of different Higgs boson production mechanisms and decays, and also by studying the particle’s kinematic properties. The ATLAS Collaboration has just presented precise new measurements of these key quantities. Several of these measurements were updated to use the full LHC Run 2 dataset (2015–2018), to provide the best precision to date.
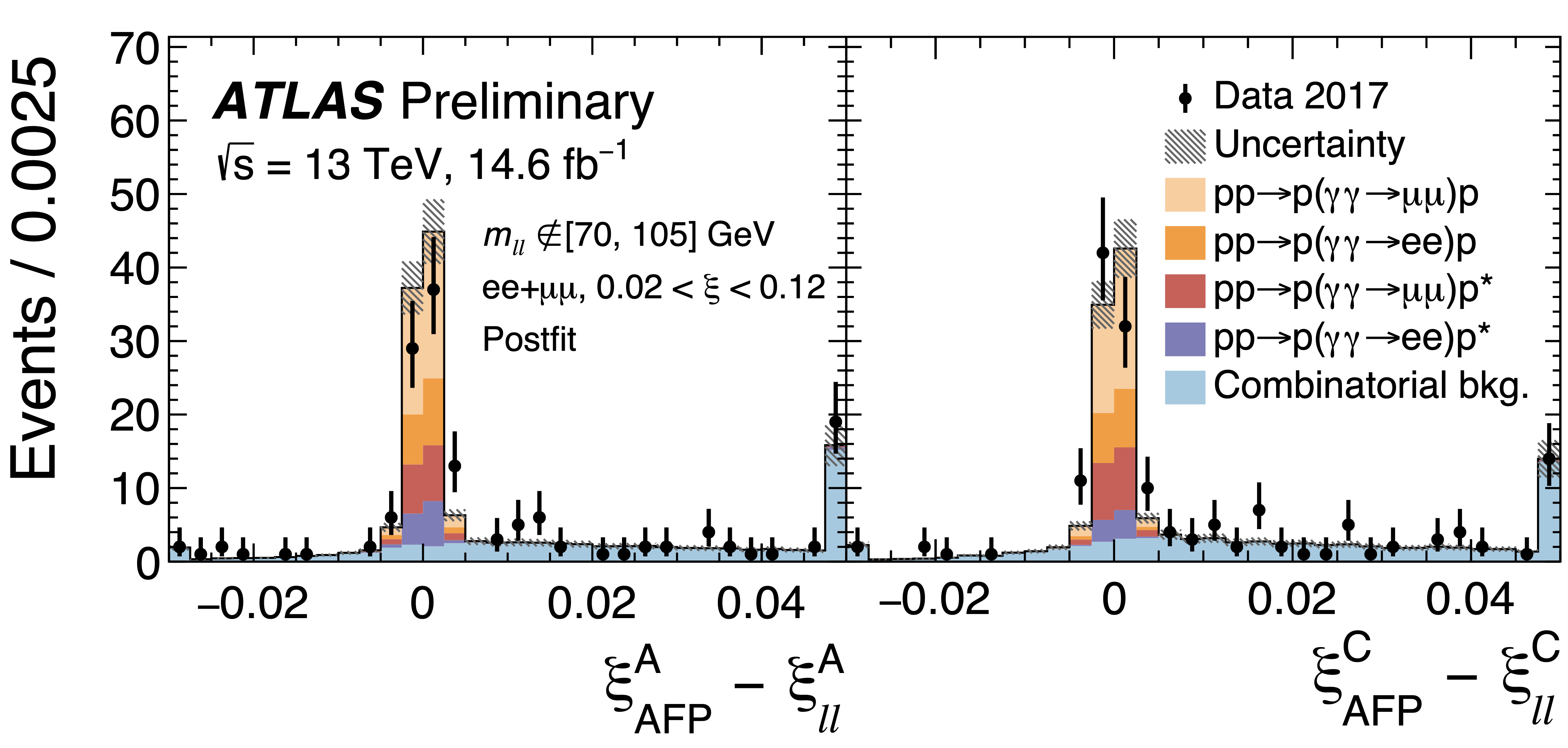
Looking forward: ATLAS measures proton scattering when light turns into matter
Today, at the International Conference for High Energy Physics (ICHEP 2020), the ATLAS Collaboration announced first results using the ATLAS Forward Proton (AFP) spectrometer. With this instrument, physicists directly observed and measured the long sought-after prediction of proton scattering when particles of light turn into matter.
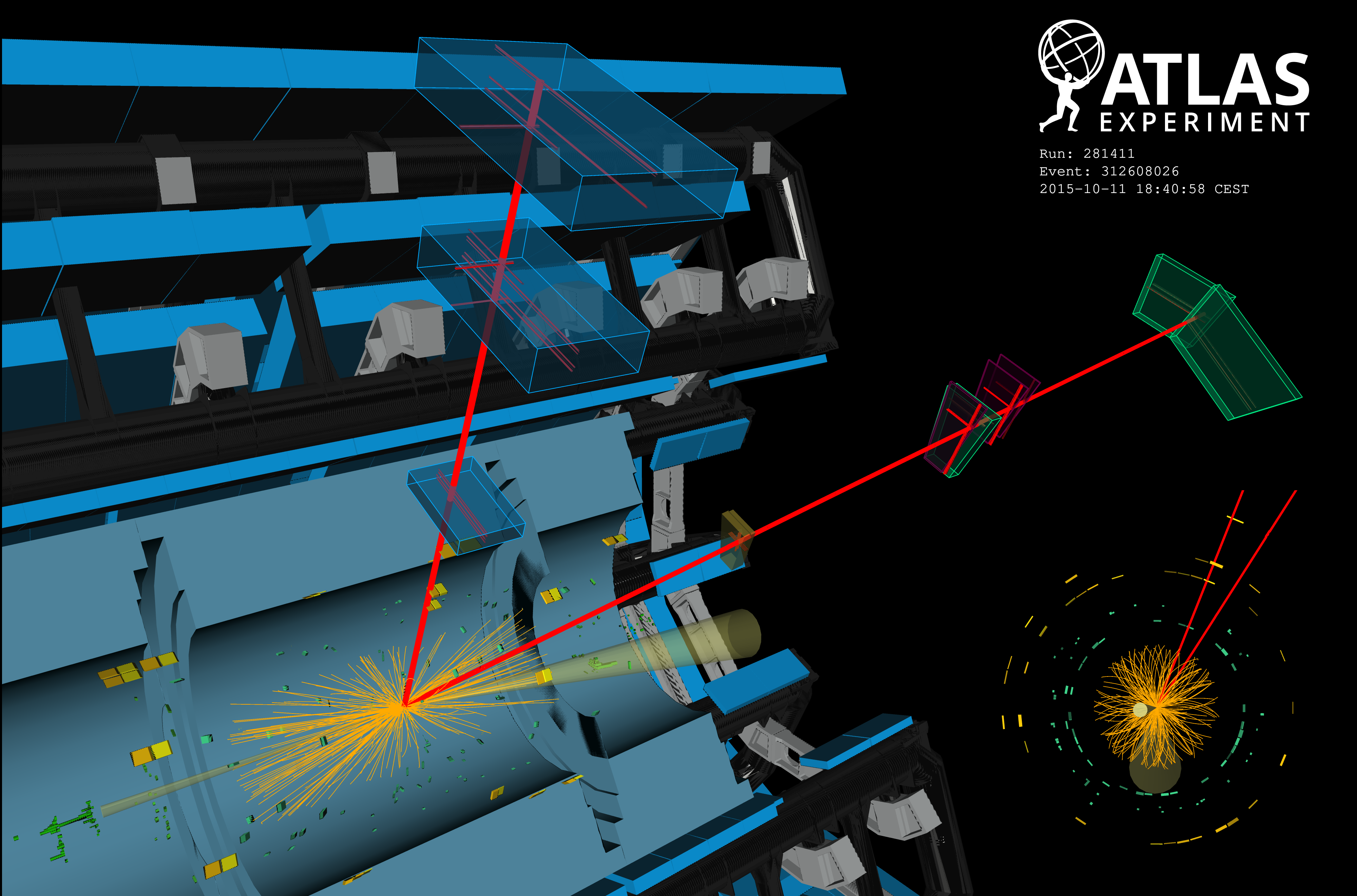
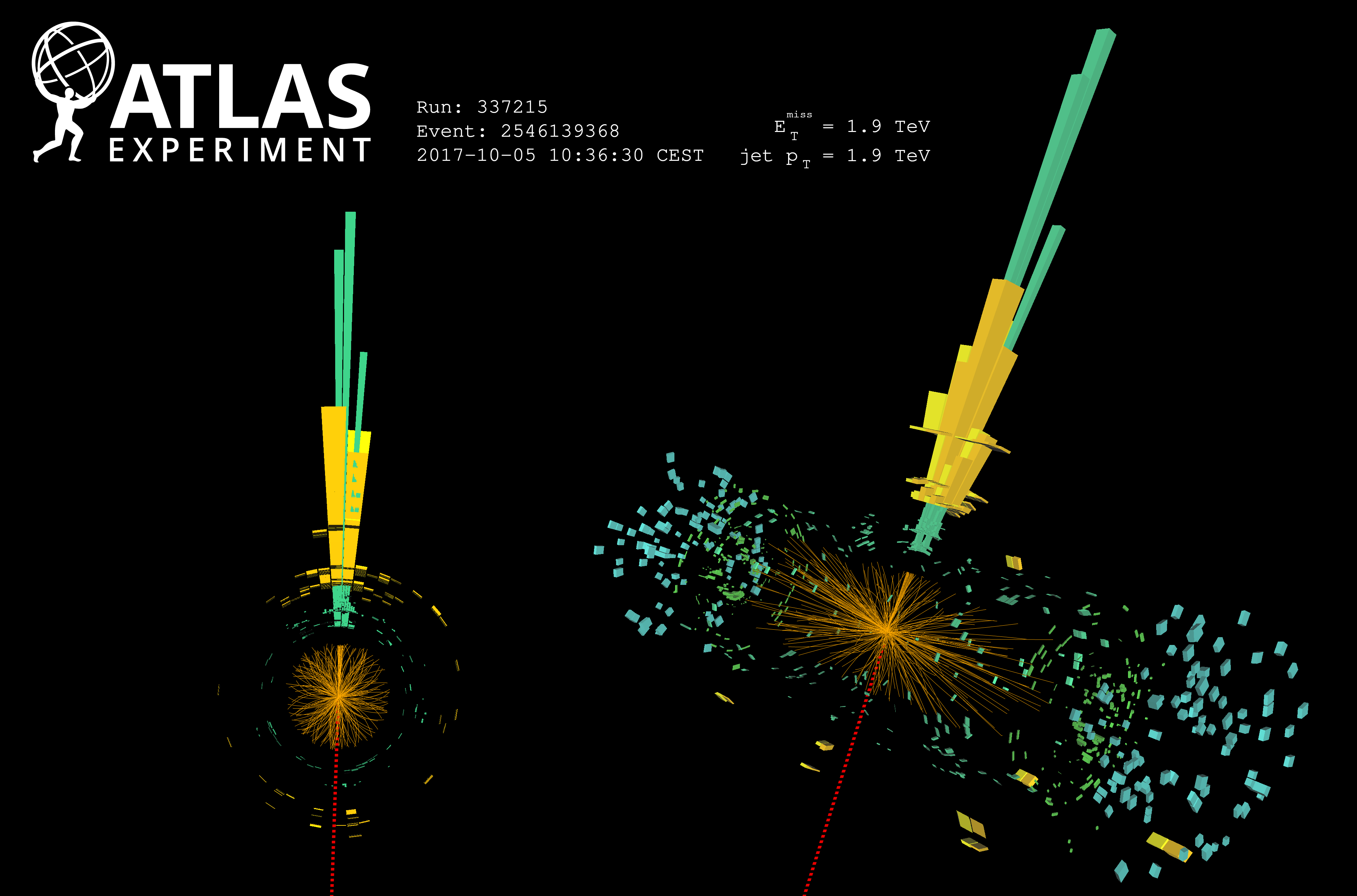
ATLAS probes interactions between heavyweights of the Standard Model
In the contest for the heaviest known elementary particle, the top quark and Z boson rank first and third, respectively. When a proton–proton collision produces a top-quark pair together with a Z boson – a process known as ttZ production – their total mass can reach an impressive 440 GeV! The discovery of this highly energetic process thus required the record collision energy and rate of the LHC; no previous collider could come close.
Jetting into the dark side: a precision search for dark matter
The nature of dark matter remains one of the great unsolved puzzles of fundamental physics. Many theoretical scenarios postulate that dark matter particles could be produced in the intense high-energy proton–proton collisions of the LHC. While the dark matter would escape the ATLAS detector unseen, it could occasionally be accompanied by a visible jet of particles radiated from the interaction point. Today, at the International Conference in High-Energy Physics (ICHEP 2020), ATLAS presented a new search for novel phenomena in collision events with jets and high missing transverse momentum (MET).
Summary of new ATLAS results for ICHEP 2020
Since the 1950s, one conference has stayed circled in red on every physicist's calendar: the International Conference on High-Energy Physics (ICHEP). The fortieth edition of ICHEP kicks off today, bringing together particle physicists, astrophysicists and accelerator scientists to share the latest news in their fields. Originally planned as an in-person event in Prague, ICHEP2020 will instead be the very first all-virtual edition of the conference.
News |